in reality, the standard template library (STL ) is a collection of C++ template classes for data structures and algorithms
in brief, It is impossible to learn c++ (STL) without proper working knowledge of data structure and algorithms
without a doubt, a novice has to learn first DSA and algorithms to study STL in C++
During competitive programming time is a valuable asset at this instant,
it is important to realize, you can use STL to overcome the problem of writing function again and again
thus, STL library has three components
- Algorithm’s
- Container’s
- Iterator’s
Algorithms
in a word, there are build in algorithms available in STL C++
such as: sort(); set_union(); binary_search(); sort_heap(); push_heap(); pop_heap(); make_heap(); merge_heap(); reverse(); copy();
Example of a sort algorithm in STL
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void show(int A[])
{
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
cout << A[i] << " ";
}
int main()
{
int A[8]= {1, 5, 6, 7, 3, 4, 2, 0};
sort(A, A+8);//sort algorithm
show(A);
return 0;
}Output
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7Iterator’s
on the positive side, Iterator’s are available in every collection
First method
vector<int>:: iterator itr;
for(itr=v.begin();itr!=v.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<endl;Second method
for(int x:v)
cout<<x<<endl;Container’s class’s
such as : vector, forward_list, list,
deque,priority_queue, stack,
set, multiset
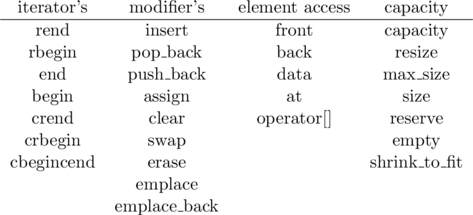
Vector class contain a different types of member functions
that is : push_back(), pop_back(), insert(), remove(), size(), empty()
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Vector of type integer
//V is an object and it is initialized with 1,2,3,4,5
vector<int> v ={1,2,3,4,5};
v.push_back(6); //Push_back member function of vector class
v.push_back(7);
//iterator class belong to a vector class
//itr is an object of iterator
vector<int>::iterator itr;
cout<<"First iterator method" << endl;
for(itr=v.begin();itr!=v.end();itr++) //First iterator method
cout<<*itr<<endl;
cout<<"Second iterator by each loop method"<<endl;
for(int x:v)//Second iterator by each loop method
cout <<x<<endl;
return 0;
}Output
First iterator method
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Second iterator by each loop method
1 2 3 4 5 6 7vector class
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
v.push_back(8);
v.push_back(9);
for(int x:v)
cout<<x<<endl;
return 0;
}Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9vector member function’s

string class
that is to say, in C++ you declare string as
string str;
for instance, in C you declare string as
char str[40];
The operators that you can use on a string

Using assignment(=), concatenation(+), insertion(>>), extraction (>>) operators
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s; //string class with object S
s ="hi "; // assignment(=) operator
string s1=" there";
string s2;
s2 = s+s1; // concatenation(+) operator
cout << s2; // insertion (>>) operator
return 0;
}Output
hi thereUsing Concatenation assignment (+=) operator on a string
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s; //string class with object S
s ="hi "; // assignment(=) operator
s+="there"; //Concatenation assignment (+=) operator
cout << s; // insertion (>>) operator
return 0;
}Output
hi thereUsing sub scripting [] operator on a string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
string s ("hi there");
for (int i=0; i<s.length(); i++)
{
cout << s[i]; // [] sub scripting operator
}
return 0;
}Output
hi thereUsing inequality(!=) operator on a string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hi_there"); // string object s1
string s2("hi_there"); // string object s2
if(s1 != s2) // inequality operator(!=)
cout<<"s1 and s2 are not equal."<<endl;
else
cout<<"s1 and s2 are equal."<<endl;
return 0;
}Output
s1 and s2 are equalUsing equality(==) operator on a string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hi_there");
string s2("hi_there_people");
if(s1 == s2)
cout<<"s1 and s2 are equal."<<endl;
else
cout<<"s1 and s2 are not equal."<<endl;
return 0;
}Output
s1 and s2 are not equalUsing Greater than (>) operator on a string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hi_there");
string s2("hi_there_people");
if(s1 > s2)
cout<<"s1 is greater than s2 "<<endl;
else
cout<<"s1 is less than s2 "<<endl;
return 0;
}Output
s1 is less than s2Using less than (<) operator on a string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hi_there");
string s2("hi_there_people");
if(s1 < s2)
cout<<"s1 is greater than s2 "<<endl;
else
cout<<"s1 is less than s2 "<<endl;
return 0;
}Output
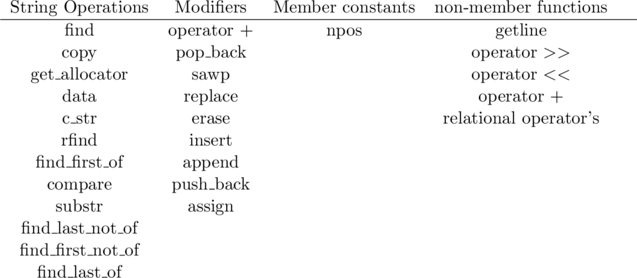
s1 is greater than s2String member functions

Assign() function
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s; //String with object s
s.assign("hi_there");//You can also directly assign by s1 = ?hi_there?;
cout<<s;
return 0;
}Output
hi_thereappend() function
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s= "hi_there";
s.append("people"); //You can also use s+= ?people?;
cout<<s;
return 0;
}Output
hi_there peopleinsert( )function
Syntax
string object.insert(pos, value)#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string obj= "hi_people";
obj.insert(2,"_there");
cout<<obj;
return 0;
}Output
hi_there_peoplereplace() function
syntax
string object .replace(pos, length,value)#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string obj= "hi_people";
obj.replace(2,7,"_there");
cout<<obj;
return 0;
}Output
hi_thereerase() function
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string obj= "hi_people";
obj.erase();
cout<<obj;
return 0;
}Output
find() function
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string obj= "hi_there_people";
int i =obj.find("there");
cout<<i;
return 0;
}returns
index value of given text
Output
3size() function
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string obj= "hi_there_people";
int i =obj.size();
cout<<i;
return 0;
}Output
15at() function
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string obj= "hi_there_people";
cout<<obj.at(4);
return 0;
}Output
hdata() function
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s1 = "hi_there";
cout<<s1.data();
return 0;
}Output
hi_therefind_first_of() function
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string obj = "hi_there_people";
cout << obj.find_first_of('t');
return 0;
}return
gives the position of the first occurrence of a given letter from the string
Output
3find_last_of() function
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string obj = "hi_there_people";
cout << obj.find_last_of('h');
return 0;
}return
gives the position of the last occurrence of a given letter from the string
Output
14c_str() function
c_str() function convert c++style string into c style string
c_str returns a const char* (which is a C style string)
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s1="hello";
cout<<s1.c_str();
}Output
helloconvert c++style string into c style string without c_str() function
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s1="hello"; // c++ string
char str[30]; // c string
strcpy(str,s1); //convert c++ string(s1) to C string(str)
cout<<str;
}Output
Error : cannot convert std::string to basic_string<char>convert c++style string into c style string with c_str() function
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s1="hello"; // c++ string
char str[30]; // c string
strcpy(str,s1.c_str()); //convert c++ string(s1) to C string(str)
cout<<str;
}Output
helloList class
Syntax

Here one, two, and three are the list objects
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> v={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
v.push_back(8);
v.push_back(9);
for(int x:v)
cout<<x<<endl;
return 0;
}Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9NOTE: you can use other container class by including header file and declaring its class
every container class have a different member functions
for an instant, forward_list class won’t have push_back member function, it has push_front member function


Leave a Reply