The blog covers the basic concepts of object oriented programming in c++
In software construction, object-oriented programming is a methodology to construct software although there are many methodologies that are available to construct software such as
- Structured programming language
- Function oriented programming language
- Aspect-oriented programming language(AOP)
- Object-oriented programming language(OOPS)
A well-known and famous methodology is an object-oriented programming language that most of the latest programming languages support oops
Concept of oops
Let us understand the concept of oops through function-oriented language such as C
Why?
because C support C++ and any valid C program is also a C++ program
The people who know C++ are well aware of C so, I will use C to explain OOPS
Suppose, if I am developing a software for school management system then, in that case, I will look at that system through a collection of function
Why?
because I am using function-oriented language such as C, where you don’t have the luxury of class and objects and you have to work with functions only to build any software system
The user of the school management system will be utilizing this set of functions to complete his tasks
So, you can develop software in the form of a collection of functions if you are using function-oriented programming
The software “school management system” will be based on a collection of function

The above figure shows an example of software development in a function-oriented language
the software called “school management system” contain four functions such as
student_name(); //first Function
student_roll_no(); //second function
student_fees(); //third function
and student_age(); // fourth function
For object-oriented programming language
such as C++ the complete software consists of a collection of objects
Where Each object will have its function and data
The user of the system will be utilizing these objects to complete his tasks
Object-oriented language is best suited for large size systems

The above figure shows an example of software development in an object-oriented language
where it contain four departments which are nothing but objects and each object will have relevant function + data
Fundamentals of object-oriented programming language
- Classes
- Objects
- reusability
- Abstraction
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
What is a class? And what is an object?
In simple terms think class as datatype [float] and object is a variable of that float data type
Class and Object
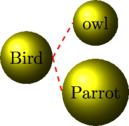
Here Bird is class and parrot and owl are the object
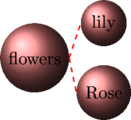
Here flower is a class and rose and lily are the object
The structure of a class contains
Two keywords
- Public
- Private
Public: means data and functions can be accessed outside the class
Private: means data and functions are hidden that it cannot be accessed outside the class by other functions
Reusability
Once you have created a class and tested then it can be redistributed to the other members of your team to use it in their code
New instances of classes can be created from existing class instead of redeveloping the existing code
It will save time for the other member of a team they won’t waste time in rediscovering the wheel instead they will focus on writing a new code
Abstraction
Think abstraction as a password or a key given to you to just login into your account without worrying about how the whole the systems works
Another example consider a laptop and the abstract for laptop is a keyboard pad through which you control the laptop
you should not need to know how motherboards work with its transistors, capacitors, resistors, microcontroller so, in a way, it reduces the complexity for you
in C++ you use the headers file without knowing all its internal function for example you use “cout” in the program to print output on the screen
here “cout” is abstract for you because you just know the “cout” and you don’t know all its internal functions that produce output on the screen
If you haven’t written any C++ program yet, then see this blog post for Writing the first C++ program
Resource
- Let us C++ by Yashavant Kanetkar
- Let us C by Yashavant Kanetkar
- Data structures using C by Reema Thareja
- https://www.udemy.com/course/cpp-deep-dive/


Leave a Reply