What is a wav file
It is an Audio file format designed for audio storage in computer files and uses a filename extension as .wav there are different sound file format available such as AIFF(Audio Interchange FILE Format) which is mostly used in macOS platform it is similar to RIFF(Resource Interchange FileFormat)
The one key difference between RIFF WAV and AIFF is RIFF is little-endian and AIFF is big-endian
Wave format is introduced by Microsoft while AIFF is introduced by Apple
To view the structure of a Wave file format
The basic concept of sound storage in computer files
A sound file provides a platform for the computer’s to manipulate audio
It also provides a device-independent way to store audio and input/output a sound generating program without worrying about complex issues like ADC/DAC
There are different type encoding is there, some sound file use compressed data while others use uncompressed data but PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) is the most common one
What’s inside a wav file
A wave file format is based on the RIFF file format and the RIFF wave sound files are chunked file format which is mostly used in window’s operating system
It is built for intel processor’s and the data is stored in little-endian byte order
Chunks are a cluster of data and each chunk have a different type of information
Each chunk have mini header contain an ID
The wav file contains three main chunk’s
- RIFF chunk
- Format sub-chunk
- Data sub-chunk
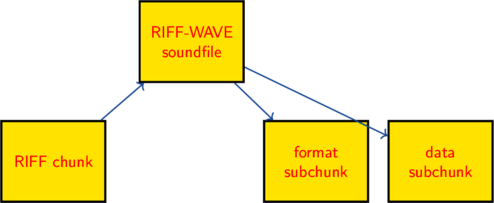
RIFF Chunk: contain’s information related to Chunk ID, Chunk data size and RIFF TYPE ID
Format sub-Chunk: contain’s information related to Chunk 1 ID, Chunk1 data size, format tag, number of channels, sample rate, Block Align and Bits per Sample
Data sub-Chunk: contain information related to Chunk2 ID, Chunk2 data size, and Sample data
Sample rate: number of samples per second
A sound file will have sample rate according to the audio data is sampled
standard sample rates are 22,050, 44100,48,000,96,000, 192,000 hertz
The use of higher sampling usually above 44,100HZ require more storage space
Audio channels
The sound file also have data related to how many channels present in an audio file
Suppose if we have an audio file, which has two channels, channel 1 (left) and channel 2 (right) then Multiple channels can exist in an audio file in an interleaved fashion
For a two-channel audio file, the data contain continuous sample frames 1 2 3 4 ……… n where Each sample frame contain samples for channel 1(left) and channel 2(right)
Interleaving
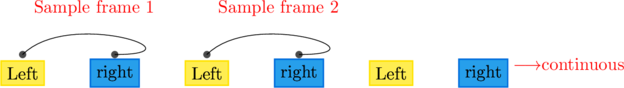
Deinterleaving
![]()


Leave a Reply