The concept structures of C and typedef struct in C is covered in this blog
Structures(records) in C
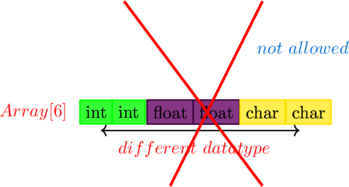
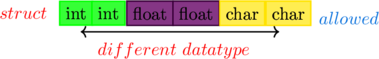
A structure is a group of variables of different data types and An array is a collection of variables of the same data types
Suppose if we have an array of 6 elements. then, it is not allowed to store 2 int , 2floats, 2char elements in an array.
if we have a struct of 6 elements. then, it is allowed to store 2int, 2floats, 2char elements in a struct
With C language, we can store similar data types with Arrays and String
to store different data types in a single name we use a keyword called struct


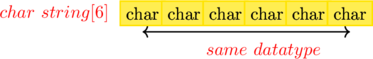
why we use structures
suppose we want to store a record of an employee
employee_name(string) employee_no(int) employee_salary(float)
to store an employee record we need to store into 3 individual array’s and it’s better to use one array of structure
Syntax

structure Declaration

Initialization of structure
Structure elements can not be initialized with the declaration

Structure elements can be initialized by using braces { }

Accessing structure elements
Access structure elements by using .operator
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
struct employee
{
char name[12];
float salary;
int employee_no;
};
struct employee e1 ={"tom",5000.45,1884};
printf("%s %f %d",e1.name,e1.salary,e1.employee_no);
return 0;
}Output
tom
5000.45
1884writing and reading a structure variable
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
struct num
{
int x, y, z;
}s;
FILE *fp;
s.x=25;
s.y=50;
s.z=100;
fp=fopen("sample.txt","wb");
fwrite(&s, sizeof(s),1,fp);
fclose(fp);
fp =fopen("sample.txt", "rb");
fread(&s, sizeof(s),1,fp);
printf("\nx=%d\ny=%d\n z= %d",s.x,s.y,s.z);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}Output
x=25
y=50
z=100Typedef
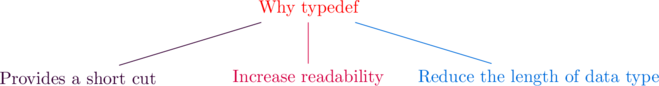
Keyword typedef is used to assign a duplicate name to datatypes
Why typedef is used?
Syntax
Typedef datatype duplicate_name;
#include <stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
typedef char string[10];
string x ="hello"; //string[10] is replaced with string x
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("%c",x[i]);
}
return 0;
}Output
helloTypedef of structures
Another way of declaring a structure is by using typedef
the main advantage of typedef of a structure is you no need to mention struct keyword every time you initialize a structure
we just need to specify the typedef in front of struct tag to create a new type

Example
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct employee_record {
char name[20];
float salary;
int employee_no;
}emp;
emp e1 = {"tom",5000.45,1884};
int main()
{
printf("\nName of the employee : %s",e1.name);
printf("\n employee salary : %f",e1.salary);
printf("\n employee_no : %d",e1.employee_no);
return(0);
}Output
name of the employee is tom
employee salary 5000.45
employee_no: 1884

Leave a Reply