The address resolution protocol (ARP) is used to know to the receivers Mac address when the sender knows its IP address
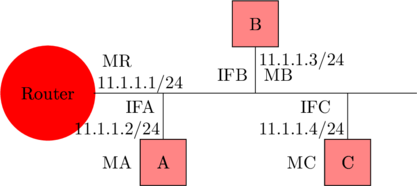
The above topology shows an L3 router with Mac address MR have three machines A, B, C with Mac address MA, MB, MC, and all the four devices including the router falls in a subnet A which have a network id 12.1.1.0/24
Let us understand practically ARP with an example
From the above topology suppose, machine A likes to send data to machine B that means machine A will be a sending machine and machine B will be a receiving machine
At this instant, machine A will not be in a position to send data to machine B until and unless it knows the B Mac address
Therefore, an ARP protocol is needed which allows machine A to know the machine B Mac address so, that machine A can talk to the machine B
Similarly, machine A should know machine C and L3 router Mac addresses to exchange data with them
ARP Table
ARP table contains the mapping of IP to the Mac address of direct neighbors here, the direct neighbors means all the machines that are available in the same subnet
So, by using ARP protocol machine A maintains IP to Mac address mapping of all other machines in the subnet, and this mapping is stored in a table called ARP table
Similarly, all the hosting machines in the topology, and L3 router which are present in the same subnet, will have a table called the ARP table
Example of ARP table of machines B and A
| IPS | Mac | oif |
| 12.1.1.1 | MC | IFB |
| 12.1.1.2 | MA | IFB |
| 12.1.1.4 | MR | IFB |
| IPS | Mac | oif |
| 12.1.1.1 | MC | IFA |
| 12.1.1.3 | MB | IFA |
| 12.1.1.2 | MR | IFA |
As you can see from the above ARP tables that it contains the mapping from IP address to Mac of all direct neighbors and also out going interfaces
An example

The above topology show the 3 machines VM, VM1, VM2 with subnet A and subnet B
ARP protocol operates only between the machines which falls in the same subnet
So, ARP will operate between machines VM and VM1
Why?
Because they have one interface each in the same subnet A(192.168.4.0/24)
Similarly, ARP will also operate between the machines VM1 and VM2 because they also have one interface each in the same subnet B(192.168.1.0/24)
ARP will not operate between the machines VM and VM2
Why?
Because they don’t have any interfaces which are operating in the same subnet


Leave a Reply